二、自定义Source
1、概述
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。官方提供的source类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些source。
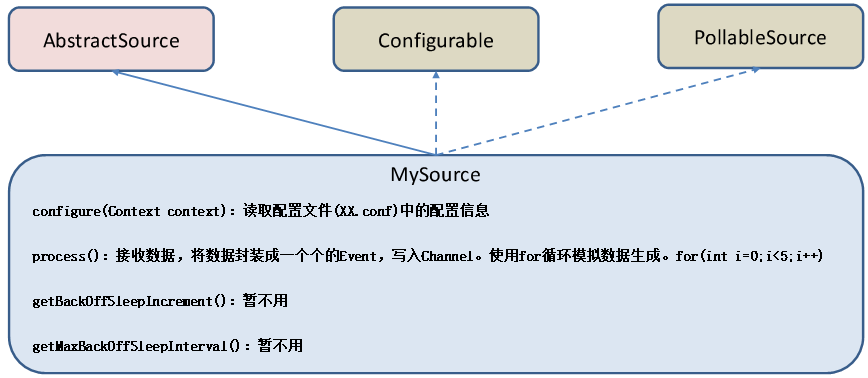
官方也提供了自定义source的接口:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source 根据官方说明自定义MySource需要继承AbstractSource类并实现Configurable和PollableSource接口。
实现相应方法:
getBackOffSleepIncrement() //暂不用
getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() //暂不用
configure(Context context) //初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
process() //获取数据封装成event并写入channel,**这个方法将被循环调用**。
使用场景:读取MySQL数据或者其他文件系统。
2、需求
使用flume接收数据,并给每条数据添加前缀,输出到控制台。前缀可从flume配置文件中配置。
自定义Source需求:
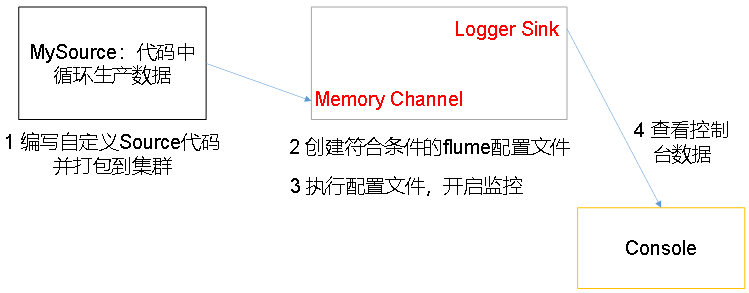
自定义Source需求分析:
3、编码
1)导入pom依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2)代码
package com;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MySource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
//定义配置文件将来要读取的字段
private Long delay;
private String field;
//初始化配置信息
public void configure(Context context) {
delay = context.getLong("delay");
field = context.getString("field", "Hello!");
}
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
try {
//创建事件头信息
HashMap<String, String> hearderMap = new HashMap<>();
//创建事件
SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();
//循环封装事件
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//给事件设置头信息
event.setHeaders(hearderMap);
//给事件设置内容
event.setBody((field + i).getBytes());
//将事件写入channel
getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event);
Thread.sleep(delay);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return Status.BACKOFF;
}
return Status.READY;
}
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
}
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
}
}
3)测试
(1)打包
将写好的代码打包,并放到flume的lib目录(/opt/module/flume)下。
(2)配置文件(mysource.conf)
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = com.MySource
a1.sources.r1.delay = 1000
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(3)开启任务
在/opt/module/flume输入命令:
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -f job/mysource.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
三、自定义Sink
1、概述
Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
Sink是完全事务性的。在从Channel批量删除数据之前,每个Sink用Channel启动一个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent,Sink就利用Channel提交事务。事务一旦被提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
Sink组件目的地包括hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、null、HBase、solr、自定义。官方提供的Sink类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些Sink。
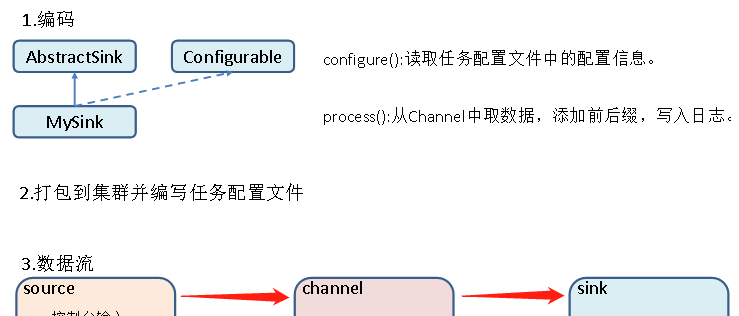
官方也提供了自定义source的接口:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#sink 根据官方说明自定义MySink需要继承AbstractSink类并实现Configurable接口。
实现相应方法:
configure(Context context) //初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
process() //从Channel读取获取数据(event),这个方法将被循环调用。
使用场景:读取Channel数据写入MySQL或者其他文件系统。
2、需求
使用flume接收数据,并在Sink端给每条数据添加前缀和后缀,输出到控制台。前后缀可在flume任务配置文件中配置。
流程分析:
3、编码
1)代码
package com;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
//创建Logger对象
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractSink.class);
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
//声明返回值状态信息
Status status;
//获取当前Sink绑定的Channel
Channel ch = getChannel();
//获取事务
Transaction txn = ch.getTransaction();
//声明事件
Event event;
//开启事务
txn.begin();
//读取Channel中的事件,直到读取到事件结束循环
while (true) {
event = ch.take();
if (event != null) {
break;
}
}
try {
//处理事件(打印)
LOG.info(prefix + new String(event.getBody()) + suffix);
//事务提交
txn.commit();
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Exception e) {
//遇到异常,事务回滚
txn.rollback();
status = Status.BACKOFF;
} finally {
//关闭事务
txn.close();
}
return status;
}
public void configure(Context context) {
//读取配置文件内容,有默认值
prefix = context.getString("prefix", "hello:");
//读取配置文件内容,无默认值
suffix = context.getString("suffix");
}
}
2)测试
(1)打包
将写好的代码打包,并放到flume的lib目录(/opt/module/flume)下。
(2)配置文件(mysink.conf)
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = com.MySink
#a1.sinks.k1.prefix = atguigu:
a1.sinks.k1.suffix = :atguigu
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(3)开启任务
在/opt/module/flume输入命令:
bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -f job/mysink.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console

